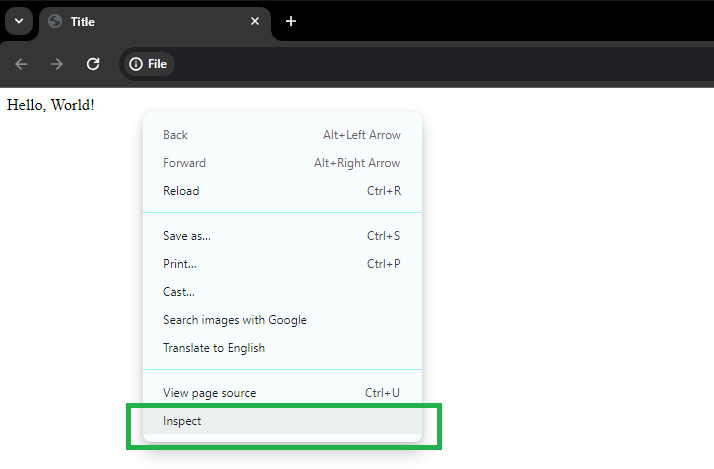
The settings forms for many activities in the Web macro Task include a tab for specifying the path to HTML element. There are three ways to specify the path to the element:
•Relative
•By position
•By search
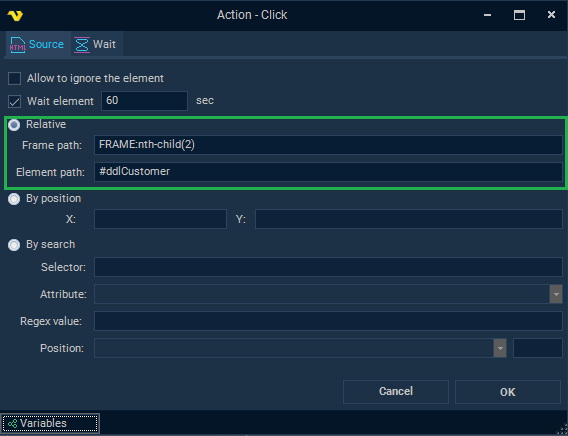
Relative mode
Element path is a field that specifies the path to the element to be detected. It is possible to use a CSS selector or an XPath expression as the path to the Element. It is enough to specify only a CSS selector in this field, but the full format of this path string is
pathCss[%]pathHtml[%]pathXPath
•pathCss is a CSS selector
•pathHtml is an additional internal format for representing the path to the Element
•pathXPath is a XPath expression
•[%] is a separator
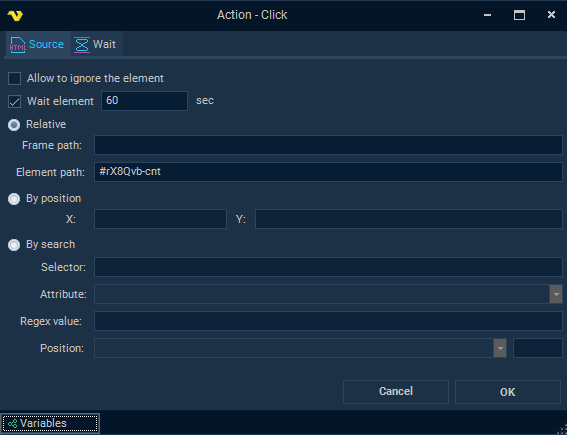
Full path format is used in recording mode for increased dependability. When configuring activities manually, the path does not need to be specified in its entirety. This path to the Element is split by the separator [%] during activity processing. The Element is first searched by the third part (pathXPath) if it exists after the split. If the Element was not found using XPath, then the element is searched using the second part (pathHtml). Finally, if the Element is still not found, the search will be using the CSS selector (pathCss). If the [%] separator is not specified, the path is interpreted as a CSS selector. To find an element using XPath, the Element path should be provided after two separators [%]. For example:
[%][%]/HTML/BODY/APP-ROOT[1]/DIV[2]/APP-RPA1[1]/DIV[1]/DIV[2]/FORM[1]/INPUT[1]
CSS selector examples
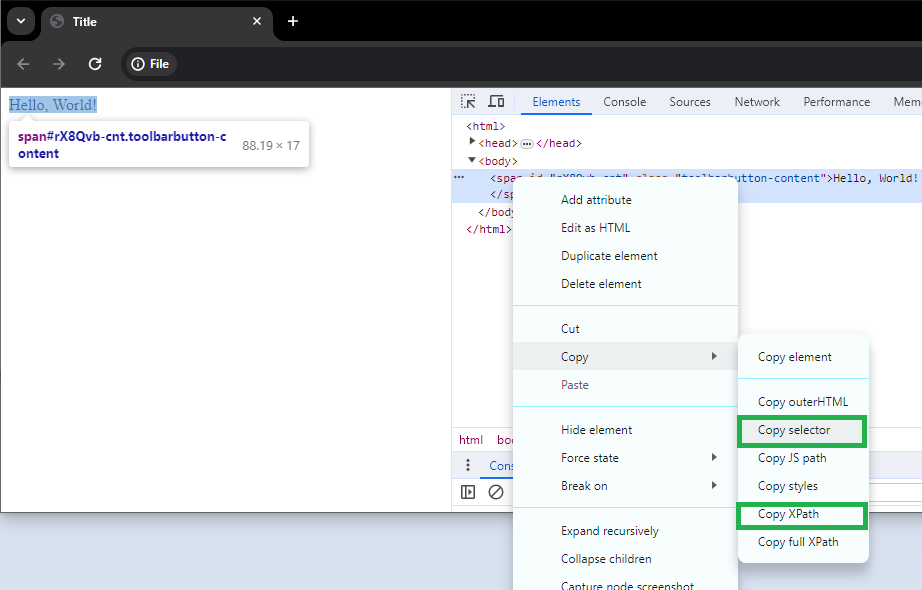
<html>
<head>
<title>Title</title>
</head>
<body>
<span id="rX8Qvb-cnt" class="toolbarbutton-content">Hello, World!</span>
</body>
</html>
In the html example above there is a span element. Examples of different CSS selectors to find this span element:
Class selector: |
.toolbarbutton-content |
ID selector: |
#rX8Qvb-cnt |
Type selector: |
span |
Attribute selector: |
span[id="rX8Qvb-cnt"] |
Child selector: |
html > body > span |
Some examples of element path using XPath:
[%][%]//*[@id="rX8Qvb-cnt"]
[%][%]/HTML/BODY/SPAN[1]
[%][%]//span[contains(., "Hello")]
Frame path is a field that specifies the path to the html tag Frame, where the path is represented as a valid CSS selector string. In most cases this field is optional. This field is only filled if the web page uses HTML frames (when the HTML web page contains a <frame> tag).
By position
Mode for locating an element by coordinates on the page. Currently out of date, upgrades are planned.
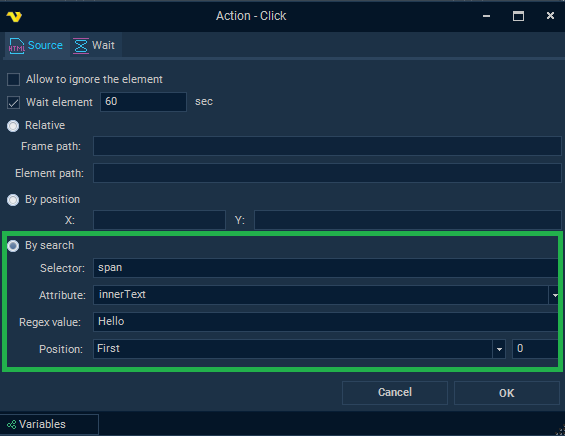
By search
This mode is based on searching for elements using a CSS selector ("Selector" field), which is passed to the JavaScript function querySelectorAll. The first step is to define a list of HTML elements that match the CSS selector. Then the resulting list of elements is filtered: the value of the specified element attribute (or element property innerHTML, outerHTML, innerText, outerText) is matched using a regular expression ("Regex value" field). Finally, the searched element is determined by the ordinal position specified in the settings ("Position" field).
Additional notes
When manually setting click activity settings, the fastest way to determine the correct CSS selector or XPath expression is to use the web browser's Inspector mode. Below is an example of using the Google Chrome browser to inspect HTML elements. Some selectors include quotes, it is important to make sure that in paths they are specified as double quotes and not single quotes.