
The Advanced Message Queuing Protocol (AMQP) is an open standard application layer protocol for message-oriented middleware. The defining features of AMQP are message orientation, queuing, routing (including point-to-point and publish-and-subscribe), reliability and security. AMQP defines a self-describing encoding scheme allowing interoperable representation of a wide range of commonly used types. It also allows typed data to be annotated with additional meaning,[17] for example a particular string value might be annotated so that it could be understood as a URL. Likewise a map value containing key-value pairs for 'name', 'address' etc., might be annotated as being a representation of a 'customer' type.
The AMQP Trigger is using the AMQP Connection.
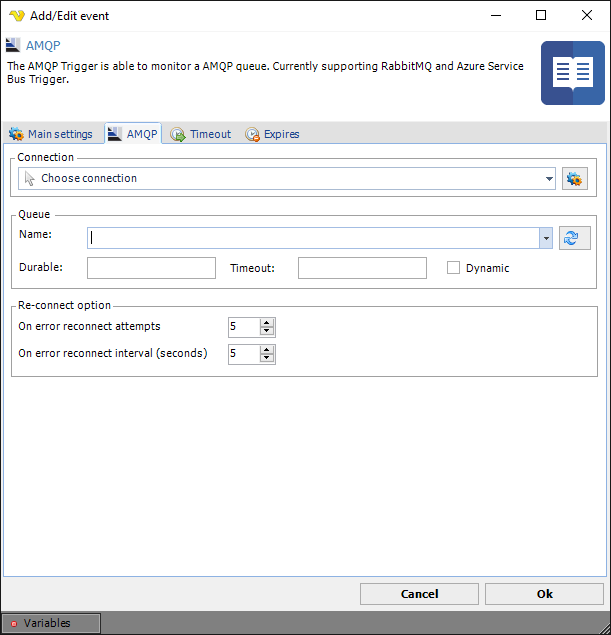
Name
Name of the queue. Click refresh to get all once you have selected a Connection.
Durable
Indicates what state of the terminus will be retained durably: the state of durable messages, only existence and configuration of the terminus, or no state at all.
Timeout
Timeout duration that an expiring source will be retained. The source starts expiring as indicated by the expiry-policy.
Dynamic
Dynamic request dynamic creation of a remote node. When set to true by the receiving link endpoint, this field constitutes a request for the sending peer to dynamically create a node at the source. In this case the address field MUST NOT be set. When set to true by the sending link endpoint this field indicates creation of a dynamically created node. In this case the address field will contain the address of the created node. The generated address SHOULD include the link name and other available information on the initiator of the request (such as the remote container-id) in some recognizable form for ease of traceability.
